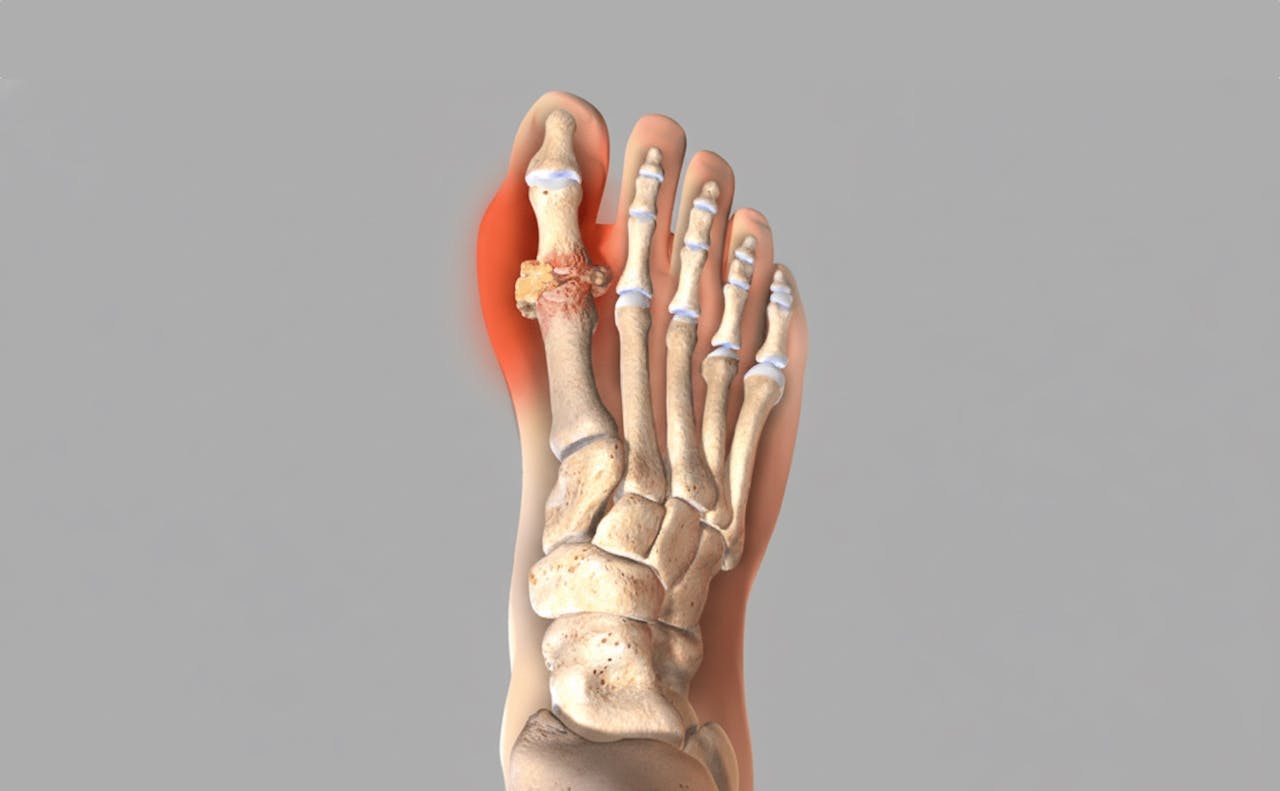
Gout
Gout is a painful form of inflammatory arthritis that typically strikes suddenly, causing intense pain, redness, and swelling, most often affecting the big toe joint.
Overview
What is it?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a build-up of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricaemia). When levels become too high, tiny, sharp urate crystals can form in and around joints. These crystals trigger a severe inflammatory response. While it can affect any joint, it classically presents in the big toe (a condition historically known as 'podagra').
How common is it?
It is highly common in the UK, affecting roughly 1 in 40 people. It is more prevalent in men, particularly as they get older, though women can also develop it, usually after menopause.
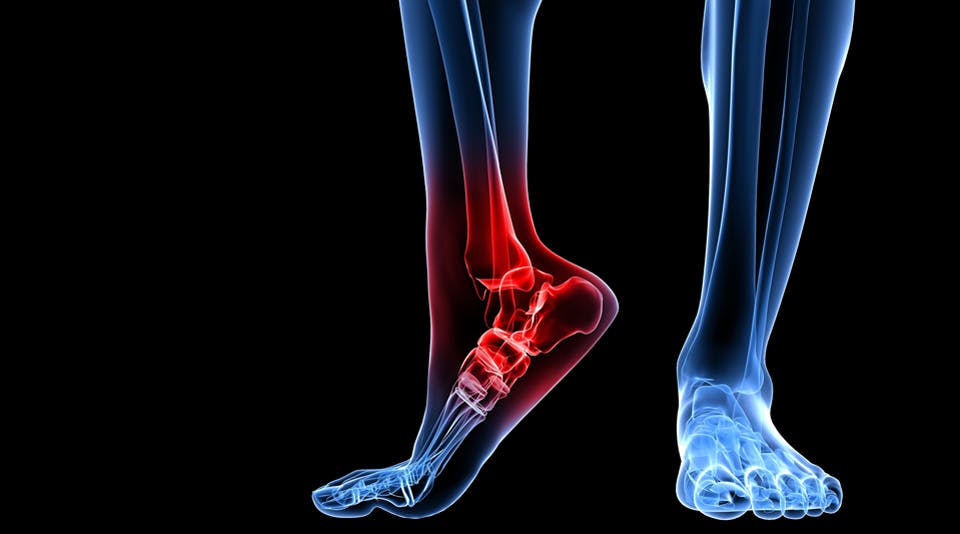
Symptoms & Causes
What are the symptoms?
Gout attacks often come on very suddenly, frequently waking patients up in the middle of the night. The affected joint becomes rapidly swollen, visibly red, shiny, and hot to the touch.
What does it feel like?
The pain is often described as excruciating—a throbbing, crushing, or burning sensation. during an acute flare-up, the joint can be so tender that even the weight of a bedsheet resting on it is unbearable.
What causes it?
The root cause is an excess of uric acid, a waste product created when the body breaks down chemicals called purines. If your body produces too much uric acid, or your kidneys do not filter enough out, it crystallises in the cooler extremities of the body (like the toes).
Triggers for an attack can include:
- Diet: High intake of purine-rich foods (red meat, offal, shellfish) and sugary drinks.
- Alcohol: Particularly beer and spirits.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can increase uric acid concentration.
- Injury: Direct trauma to a joint can sometimes trigger a flare.
Some health conditions can include:
Gout is often associated with other metabolic conditions, including:
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Kidney disease (reduced ability to clear uric acid).
- Diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Obesity.

How is it Diagnosed?
At Foot Factor, we are often the first port of call for sudden foot pain and can readily identify likely cases of gout, differentiating them from structural issues like bunions or fractures.
What tests are used to diagnose it?
- Clinical Examination: The presentation of gout is often so classic (sudden onset, hot red big toe) that we can diagnose it strongly based on history and visual inspection.
- Blood Tests: We will usually refer you to your GP for a blood test to measure your serum urate levels. Note: Uric acid levels can sometimes appear normal during an acute attack, so testing is often repeated once the flare has subsided.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: In hospitals or specialist settings, a sample of fluid might be taken from the joint to look for crystals under a microscope, though this is rarely needed for a standard diagnosis in our clinic.
Foot Factor provides Expert Podiatry Treatment Tailored to You.
At Foot Factor, our podiatrists specialise in diagnosing and treating foot pain with precision and expertise. With advanced gait analysis, bespoke orthotics, and sports-focused podiatry care, we don’t just identify the problem—we provide a targeted solution to get you back to moving pain-free. Book a consultation today and take the first step toward lasting relief.

How is it Treated?
Effective gout management requires a two-pronged approach: managing the acute foot pain immediately and long-term medical management to prevent future attacks.
- Immediate Podiatric Care:
- Offloading: During an attack, walking is difficult. We can provide advice on temporary footwear changes or padding to keep pressure off the painful joint.
- Acute Advice: We will guide you on standard acute management, such as rest, elevation, and the safe use of ice packs to reduce local inflammation.
- Medical Management (via GP):
- We will strongly advise you to see your GP for medication to treat the acute flare (such as NSAIDs, colchicine, or corticosteroids) and potentially for long-term preventative medication (like allopurinol) if attacks are frequent.
- Long-Term Podiatry & Orthotics:
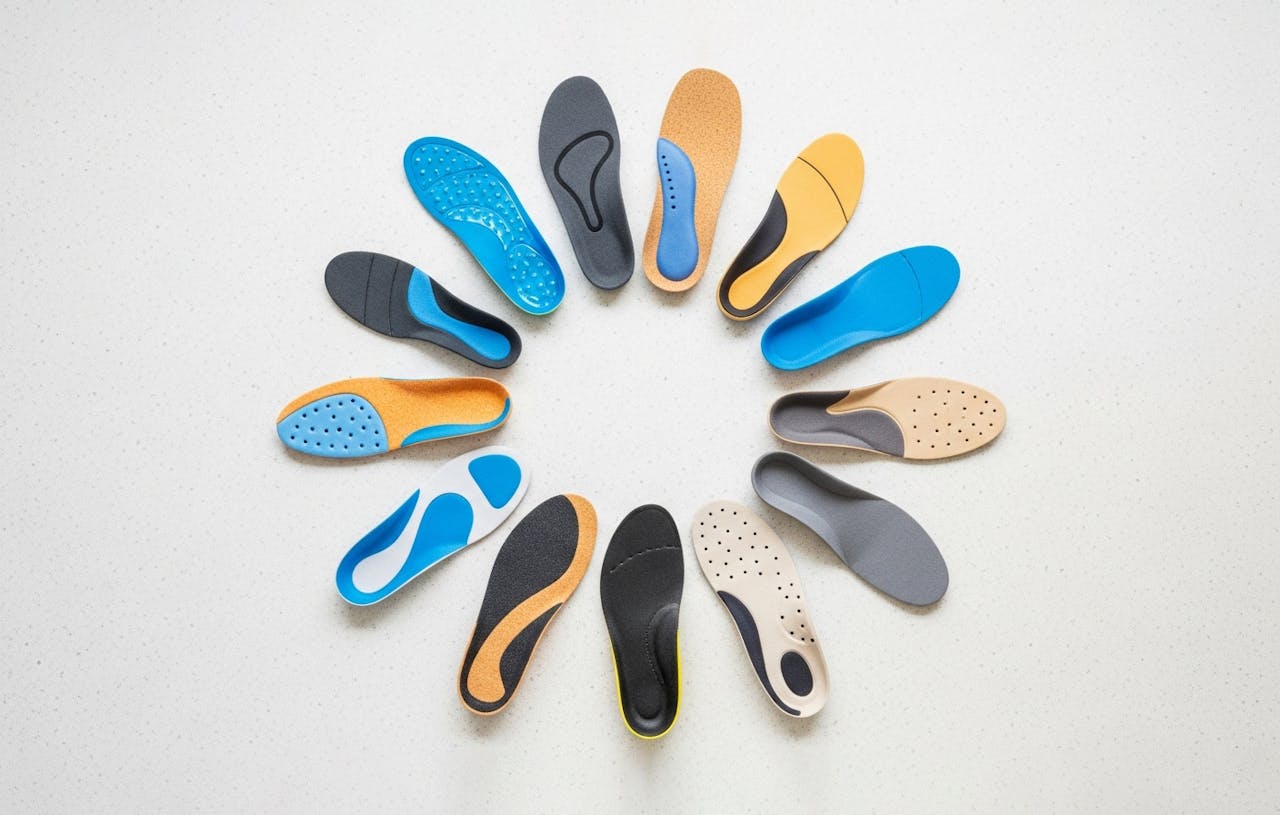
- Chronic Gout Management: Repeated gout attacks can damage the toe joint, leading to permanent arthritis and stiffness (Hallux Limitus/Rigidus). We can treat this long-term damage with specialised custom orthotics that stiffen the shoe and reduce the need for the painful joint to bend while walking.
- Footwear: Advising on shoes with adequate depth and width to accommodate any permanent joint changes or tophi (hard lumps of urate crystals that can form under the skin).
Our Bespoke Orthotics give you the Right Support for Long-Term Relief.
At Foot Factor, our podiatrists specialise in diagnosing and treating foot pain with precision and expertise. With advanced gait analysis, bespoke orthotics, and sports-focused podiatry care, we don’t just identify the problem—we provide a targeted solution to get you back to moving pain-free. Book a consultation today and take the first step toward lasting relief.
Related Articles
Find expert tips, advice, and insights to support your foot health and active lifestyle.


